Your cart is currently empty!
Carbon Credit Creation Project
Protecting the Earth’s environment alongside our future.

2
Years Cycle
Each cycle of moringa cultivation lasts two years, and carbon credits are generated every two years.
10+
Years Continuation
The project can be sustained for 5 cycles, totaling over 10 years, with continuous achievements expected throughout this period.
135+
Tons
Over 2 years, 1 hectare of Moringa trees absorbs approximately 135 tons of carbon dioxide.
15,000+
Value
The carbon credits from 1 hectare will have a value of over $15,000 over 2 years.
Project Overview
Our project leases land in Southeast Asian countries to plant Moringa trees (Moringa oleifera), which grow rapidly and reach a harvestable state within 2 years. The project operates on a two-year cycle and provides continuous achievements for five cycles, or 10 years:
- Carbon Credit Generation: Moringa trees absorb CO2 as they grow, and carbon credits are issued based on this absorption. These credits can be traded on international markets.
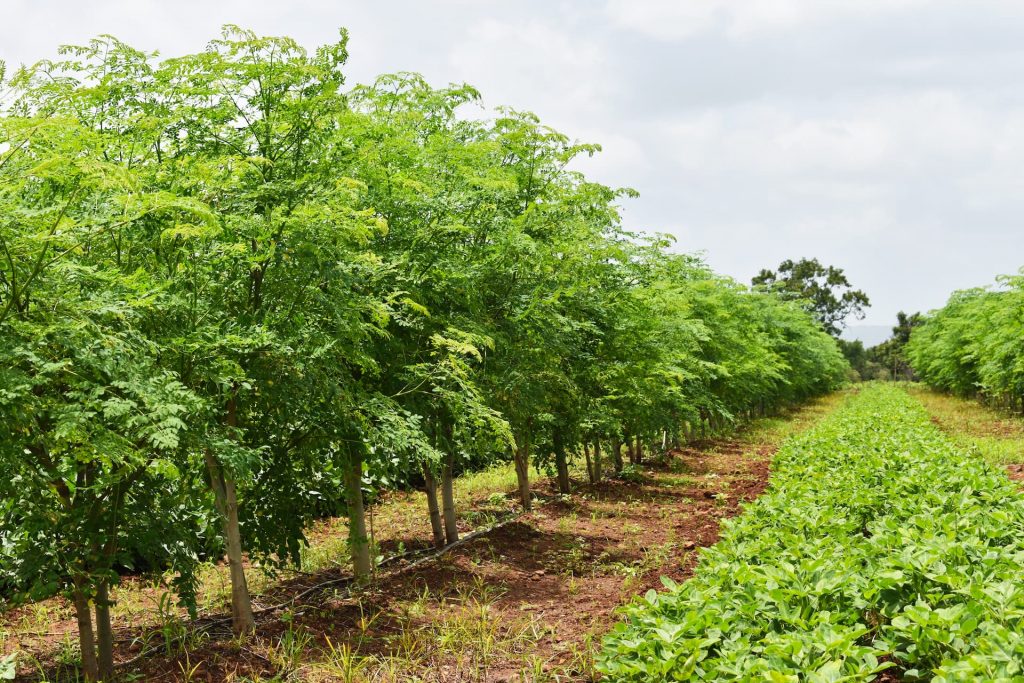

Carbon Credits and Other Utilization
This project not only focuses on carbon credit generation but also utilizes harvested Moringa leaves as a health food product, while the wood can be used as biomass fuel. By partnering with organizations dedicated to environmental protection, it helps reduce the impact on the planet and contributes to the local economy.
Track the Project’s Progress Online
Participants can monitor the project’s progress in real time through a dedicated website. You can access information about the land, tree growth status, carbon credit issuance, and more at any time.
A Gift for the Environment and the Future
This project plays a crucial role in combating global warming. By participating, you contribute to a sustainable future for the next generation. Additionally, the project serves as a meaningful way to reward yourself for your hard work or to celebrate special occasions, such as a child’s birthday, with a unique and eco-friendly gift.
The Importance of Carbon Credits
- Expanding Market: With increasing awareness of climate change, the demand for carbon credits is growing rapidly. The market is expected to continue expanding as carbon credits play a vital role in environmental efforts.
- Sustainable Future Endeavors: Through this project, you can actively participate in protecting the Earth, ensuring a healthier planet for future generations while reaping long-term benefits from carbon credits.

Global Impacts of Climate Change
Climate change is not only affecting Japan but also having a wide-ranging impact worldwide. Below is an overview of the major effects across different regions and sectors.
Frequent Heatwaves and Increased Health Risks
The global average temperature is rising, leading to record-breaking heatwaves in many regions. In Europe, summer heatwaves have become frequent, with temperatures exceeding 40°C in countries like France and Spain. This has resulted in increased mortality rates from heatstroke and cardiovascular diseases. In developing countries, high temperatures have reduced agricultural productivity in rural areas, causing significant economic losses.
Increase in Extreme Weather Events
- Intensified Hurricanes and Cyclones
In the United States and the Caribbean, hurricanes are becoming more intense due to climate change, leading to large-scale floods and damage. Hurricanes like Harvey and Irma in 2017 caused record-breaking destruction. - Frequent Heavy Rainfall and Flooding
In South Asia, changes in monsoon patterns have increased the frequency of heavy rains, causing annual flooding in countries like India and Bangladesh. This has resulted in infrastructure destruction and a rise in the number of displaced people.
Rising Sea Levels and Threats to Island Nations
Rising sea levels caused by climate change are having a severe impact on low-lying countries and island nations. Countries like Tuvalu and the Maldives face coastal erosion and more frequent storm surges, threatening their living environments and forcing many residents to relocate.
Impacts on Agriculture and Food Supply
- Drought and Declining Crop Yields
Droughts are becoming more frequent in Africa and the Middle East, destabilizing food production. Grain yields, in particular, have decreased significantly, exacerbating food shortages and famine. - Decline in Crop Quality
In countries known for wine production, such as France and Italy, high temperatures and abnormal weather patterns are affecting grape quality, forcing traditional agriculture to adapt.
Loss of Ecosystems and Biodiversity
- Melting Ice Sheets in the Arctic and Antarctic
Ice sheets in the Arctic are rapidly melting, threatening habitats for species like polar bears and seals. In the Antarctic, the accelerated shrinking of ice sheets is contributing to rising sea levels. - Increase in Forest Fires
In regions like Australia and the Amazon, drying conditions caused by climate change have led to frequent forest fires, resulting in biodiversity loss and increased carbon dioxide emissions.
Economic Impacts
The frequent occurrence of disasters and infrastructure damage caused by climate change is having a significant impact on the global economy. In developing countries, rising recovery costs are straining national budgets, while in developed countries, rising insurance premiums and industrial changes present significant challenges.
Climate change affects regions in different ways, creating a complex array of problems. Addressing these issues requires global cooperation and prompt action.

Wildfires and Their Connection to Climate Change
Climate change is increasing the frequency and scale of wildfires globally. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and altered precipitation patterns are working together to elevate wildfire risks.
Major Affected Regions and Examples
- Amazon Rainforest (Brazil)
Known as the “lungs of the Earth,” the Amazon is a crucial forest ecosystem. However, wildfires are increasing due to a combination of climate change and human-driven deforestation. High temperatures and drying conditions create an environment prone to fires, leading to widespread forest destruction. As a result, the Amazon’s ability to absorb carbon dioxide diminishes, exacerbating climate change in a vicious cycle. - Australia
In Australia, rising temperatures and decreased rainfall have intensified drying conditions, causing large-scale wildfires during summer. The “Black Summer” fires of 2019-2020 burned approximately 18 million hectares, releasing over 30 million tons of carbon dioxide. These fires also destroyed habitats, severely impacting wildlife such as koalas and other endangered species. - California (United States)
California is one of the world’s most wildfire-prone areas. Climate change has led to earlier snowmelt and extended dry seasons, making vegetation drier and more flammable. Recent fires have resulted in widespread destruction of homes, mass evacuations, and economic losses amounting to billions of dollars.
Broad Impacts of Wildfires
- Impact on the Atmosphere
Wildfires release vast amounts of carbon dioxide and particulates into the atmosphere, intensifying the greenhouse effect and accelerating climate change. Additionally, the smoke and particulates cause air pollution, leading to respiratory illnesses and other health problems. - Impact on Ecosystems
Wildfires destroy habitats, disrupting the balance of ecosystems. Some plant and animal species cannot adapt to post-fire environments, increasing the risk of extinction. Furthermore, nutrients in the soil are often lost, and it can take decades or even centuries for ecosystems to recover. - Economic Losses
Wildfires cause significant economic damage, including the destruction of homes, the cost of setting up shelters, and the expense of recovery efforts. In areas where agriculture or tourism is a major industry, reduced income can have long-term impacts on local economies.
The Vicious Cycle of Climate Change and Wildfires
Wildfires are both a cause and a consequence of climate change, creating a dangerous feedback loop. The process unfolds as follows:
- Climate change increases wildfire risk (higher temperatures, drying conditions, reduced rainfall).
- Wildfires occur, releasing large amounts of greenhouse gases.
- The released greenhouse gases further accelerate climate change, increasing wildfire risks.
Wildfires are a global issue closely tied to climate change. Immediate and long-term responses are essential to prevent devastating impacts on natural environments and to address this pressing challenge effectively.
Unique Value of the Project
Future Indicators: Contributing to the Earth’s Well-Being: Economic activities will increasingly be measured by their environmental impact. Participating in this project prepares individuals and businesses for a future where environmental stewardship is a key indicator of success.
Beyond Conventional Investment: Our project is not just an investment; it supports sustainable activities aimed at reducing CO2 and utilizing wood resources. The project is focused on environmental preservation, creating value that goes beyond financial returns.
Supporting Sustainability and Environmental Contributions: Project participants can track their contributions to environmental protection, reflecting on their role in creating a more sustainable future.
Responsibility and Pride for Future Generations
Protecting the environment is something we can be proud to pass on to future generations. By taking action now, we prepare to leave behind a healthier planet for our children and grandchildren.
Results and Future Potential
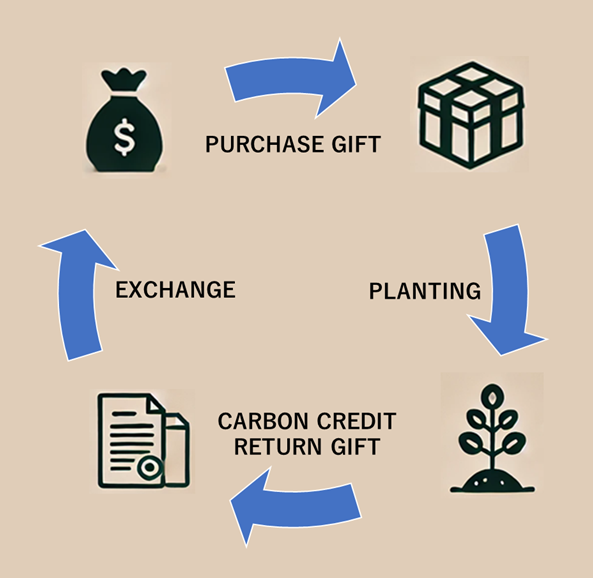
As a result of the project’s activities, there is a future potential for carbon credits to be sold on the market. The profits from this sale can be reinvested to further contribute to the success of the project, used as a reward for yourself for your hard work, or serve as a wonderful choice for special events or celebrations for your loved ones.
Preparing for the Future Now
Joining this project allows you to not only reap financial rewards but also play a part in environmental conservation. Start now, and together we can build a sustainable future for generations to come.
